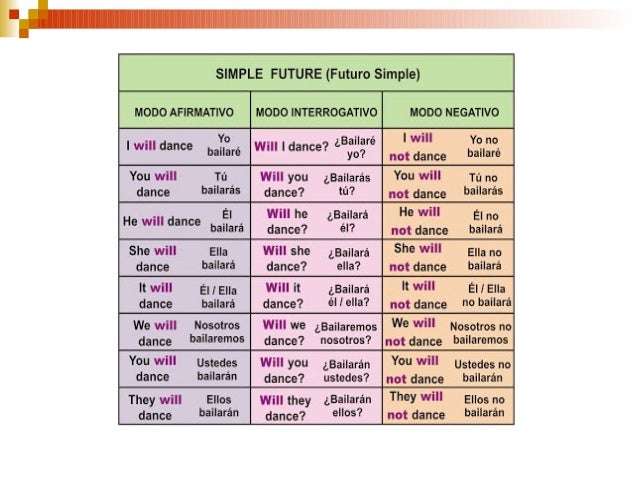
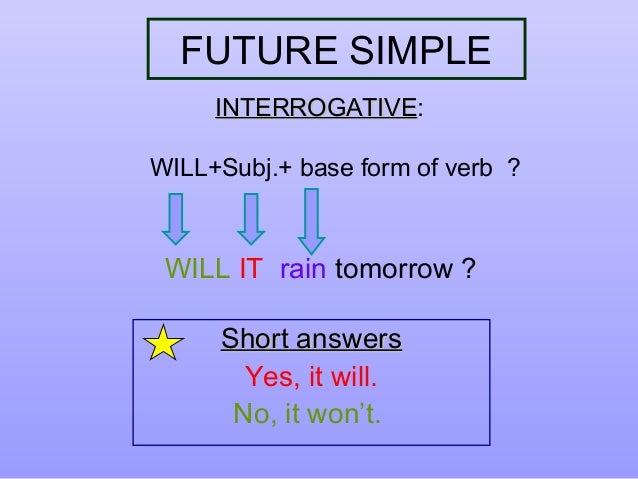
PHRASAL VERBS
Definition
A phrasal verb is a VERB+PREPOSITION/ADVERB combination.
It is very common to place
prepositions or adverbs after certain verbs so as to obtain a variety of
meanings.
examples:
give away - give to
someone / anyone
give up - abandon (a habit
or attempt)
look after - search for,
seek
look out - beware / be careful
Whether a preposition or
adverb is used is not important. What is
important is to understand the phrasal verb as a complete expression.
1. Multiple meanings
It is possible for a phrasal
verb to have more than one meaning.
eg. take off (remove
or rise from the ground)
- He took off his coat.
- The plane took off half
an hour late.
2. Transitive or Intransitive
Verbs
Transitive verbs require
an object.
eg. I am looking for my
wallet.
Intransitive verbs cannot
have an object.
eg. Look out!
You're going to fall!
3. Transitive expressions
Noun objects are usually
placed at the end of these expressions.
eg. He took off his coat.
However, with some
expressions, they can also be placed immediately after the verb.
eg. He took his
coat off.
4. Pronoun Objects
Pronoun objects can sometimes be placed at the end of an expression.
eg. We are looking for them.
It is, however, more
common for them to be placed after the verb.
eg. He took it
off.
This position is usual
before the following short words:
up, down, in, out, away, off and on
(except when used in the expression call on - visit).
eg. I'll give away these toys. I'll give them away.
5. Verb Objects
When these expressions are
followed by a Verb Object and preceded by a preposition, the gerund form of
the verb is used.
eg. He kept on whistling loudly.
CLICK ON THE LINKS
WORKSHEETS
ONLINE ACTIVITIES